Projected Medical Cost Trend Increase in 2026
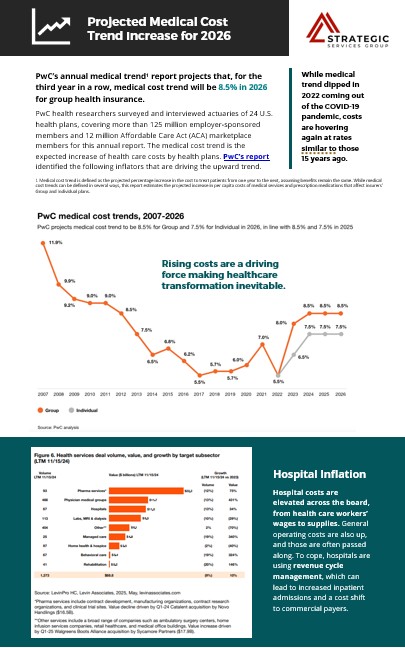
PwC’s annual medical trend report predicts that, for the third year in a row, medical cost trend will be 8.5% in 2026 for group health insurance. While medical trend dipped in 2022 coming out of the COVID-19 pandemic, costs are hovering again at rates similar to those 15 years ago. Continue reading a brief summary of the PWC Behind the Numbers report1.
By leveraging predictive analytics, health plans can identify trends in claims data to address potential cost drivers early.
- Medical Costs are Projected to Rise ➡️ 8.5% for Group plans and ➡️ 7.5% for Individual plans in 2026. This increase is fueled by continued inflation in hospital services, behavioral health, and prescription drugs—particularly GLP-1s and marks the third consecutive year of elevated trends, matching pre-ACA era highs.
- Structural cost drivers are accelerating — Wage growth, provider consolidation, and costly new therapeutics (like GLP-1s, gene and cell treatments) are inflating claims without meaningful offsets.
- Behavioral health claims are surging — +80% inpatient, +40% outpatient since 2023. This 44.6% increase is straining budgets and demands integrated, proactive strategies.
- Pharmacy cost containment require urgent attention — Prescription drug spend rose $50B in 2024. GLP-1 medications (Ozempic, Wegovy, Zepbound) are expected to impact trend by up to 1%. Employers need smarter pharmacy benefit models, including prior authorizations and value-based contracting.
- Biosimilars and AI hold promise—but require action — Health plans can curb costs by aggressively adopting biosimilars and applying AI for smarter utilization and claims management.
- Federal funding shifts will increase employer burden — Policy changes (OBBB) will reduce Medicaid and ACA subsidies, pushing more individuals into employer-sponsored plans and providers shifting cost burdens to commercial plans.
Bottom line: Employers must take the lead — Success depends on setting clear cost targets, pushing for accountability in GLP-1 oversight, behavioral health integration, and pharmacy strategies. Traditional tactics like reactive negotiations and plan tweaks are no longer enough.
PwC’s report identified the following inflators that are driving the upward trend.
Top 3 Cost Drivers (Inflators)
1. Hospital & Provider Costs
- Wage inflation, staffing shortages, and rising supply costs.
- Hospitals using advanced Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) to increase collections.
- Commercial payers absorbing more costs as Medicare and Medicaid rates lag.
2. Prescription Drug Spend
- Drug spending in the US grew by $50 billion from $437 billion to $487 billion (11.4%) in 2024 at net manufacturer prices, up from $20 billion of growth (4.9%) in 2023 (Figure 9).
- From the therapeutic area perspective, Oncology, immunology, cardiovascular, obesity and diabetes have led the growth of drug spending, totaling $37 billion.
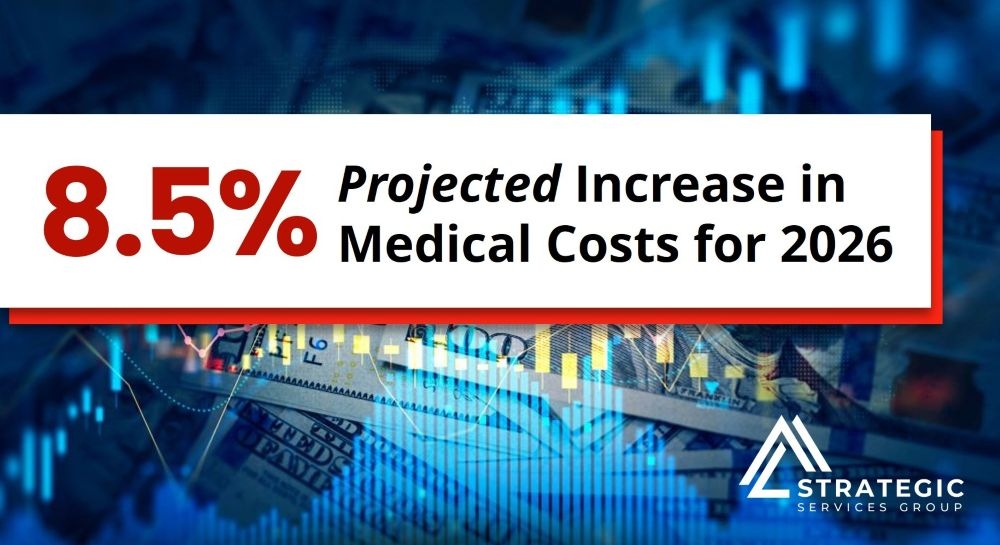
- New therapeutics, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, continue to hit the market for both prevalent chronic illnesses and rare genetic disorders.
- Looking ahead, the therapeutic pipeline is robust with potential new therapies and expanded indications.
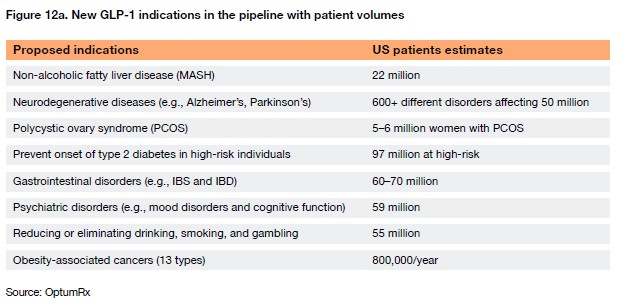
3. Behavioral Health Utilization
- Inpatient BH claims ➡️up ~80% from 2023–2024.
- Outpatient BH claims ➡️up nearly 40%.
- Employers face cost pressure as demand rises and provider shortages persist.
Top 2 Medical Cost Deflators
1. Biosimilars
- Biosimilars were noted as health plans’ top cost deflator for the third year in a row. Biosimilar adoption increased significantly in 2024, and it’s expected to continue with newly approved biosimilars for drugs such as, Humira and Stelara.
- To date, seven Stelara biosimilars have received FDA approval, launching with Wholesale Acquisition Cost (WAC) list prices more than 80% lower than the reference product.
- A similar private-label dynamic seen with Humira biosimilars is emerging as well, with two of the three largest pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) having either launched or announced plans to launch private-labeled versions.
These developments are expected to exert meaningful downward pressure on specialty drug spending and help moderate medical cost trend in the near term.
2. Smarter Cost of Care Management
- AI-powered tools improving claims integrity, fraud detection, and care management.
- Targeted utilization management and pharmacy benefit audits delivering savings.
Federal & Market Forces to Watch
Signed in 2025, The One Big Beautiful Bill (OBBBA) policy is set to:
- Reduce federal Medicaid spending by $325B;
- End enhanced ACA subsidies by late 2025;
- Impose potential pharmaceutical import tariffs.
Employer Insights & Action Steps
- Evaluate Pharmacy Strategies: Consider PBM carve-outs, GLP-1 utilization oversight, and value-based contracts.
- Modernize Plan Design: Explore innovative models (e.g., ICHRAs, transparent copay-only plans) to control costs and improve employee satisfaction.
- Partner for Performance: Hold vendors accountable for trend management—especially in behavioral health and specialty Rx.
- Use Data Strategically: Leverage claims analysis and benchmarking to inform negotiations and optimize plan performance.
Strategic Services Group (SSG) Benefits Advisors are ready to help employers shift to a strategic, end-to-end cost management approach—one that prioritizes long-term planning, accountability, and innovation across every facet of the benefits program.
SOURCE: PwC health researchers surveyed and interviewed actuaries of 24 U.S. health plans, covering more than 125 million employer-sponsored members and 12 million Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace members for this annual Behind the Numbers 2026 report.

 Prev
Prev